
Table of Contents
1) Overview
2) Web App
3) Web API
4) The JSON Schema
5) Sample Software
6) FAQ
7) Roadmap
8) Release Notes
1) Overview
KELLER’s «myCalibration» is a data-platform for KELLER customers. Via KELLER «myCalibration», customers can access digital calibration data of their KELLER sensors.
Data
Contents
«myCalibration» is designed with data from various KELLER transducers and transmitters in mind. As an example, it can be used to hold information of Mathematical Compensation Models as well as X-line transmitter calibration data.
Format
Calibration data is available in JSON file format. Thanks to its widespread use and a broad availability of programming libraries, this format allows for an easy and quick integration in customer software. What is more, as a quick check, JSON data can be inspected in any text editor.
Structure
The structure of the JSON file is defined in a JSON schema. This schema is made publicly available, allowing a full integration in customer software.
Access
Web App
A user interface that is accessible over any standard web browser gives customers access to calibration data of their sensors. Customer data is only accessible after an individual login and cannot be seen by others. After using various search and filter functionalities, the user can download calibration data of individually selected sensors or perform a bulk download of multiple datasets.
Web API
A REST API is available for automated access. Customers can integrate this API into their processes. This allows them e.g. to automatically download the calibration data of newly received sensors and integrate this into their production processes.
2) Web App
The web app is here: https://mycalibration.azurewebsites.net/
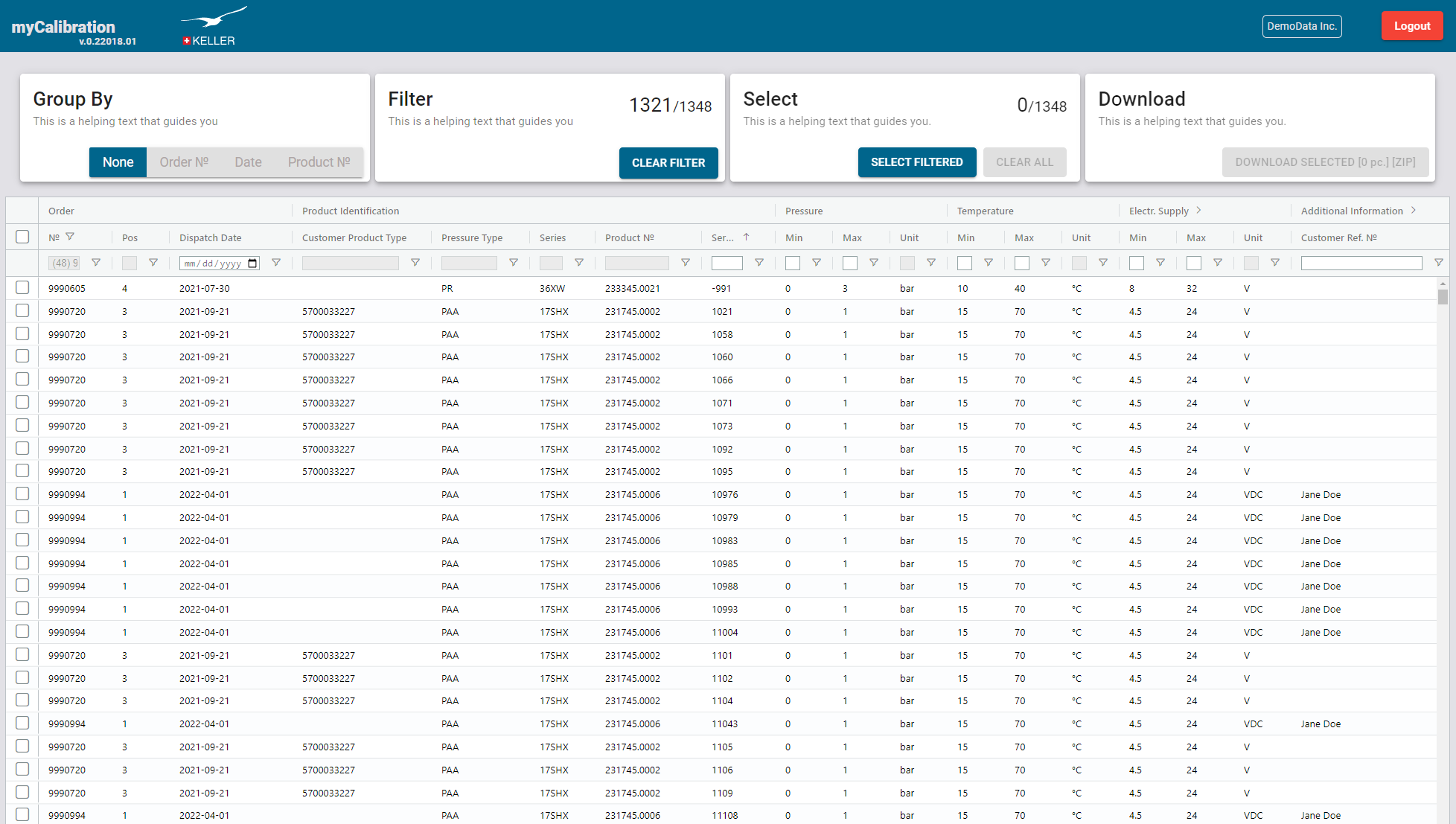
There is a free demo user account with the username ‘Demo1234’ and the password ‘Demo1234’.
Sign Up & Sign In
Signing up a user account can be done by pressing the [Sign Up] and following the instructions. A user name, an email address and accepting the ‘Terms & Condition’ is necessary.
For just testing out myCalibration without a signing up an account can be done with a free demo account ‘Demo1234’ with the password ‘Demo1234’ in order to see some demo data.
3) Web API
The Web API’s URL is https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net
The OpenAPI specification page is: https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/swagger/index.html
All the calibration data can be exported as
- JSON meta-information (header only)
- zip file with the filtered and compressed JSON files (header+data)
The Swagger JSON file can be found here: https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/swagger/v1/swagger.json
Most important API endpoints
GET /v1/CalibrationData/Headers
Responds with the meta-information(header-part) about accessible calibration data. See Header data.
| Name | Located in | Description | Required | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| skip | query | OPTIONAL. Skips the given number of rows. The opposite of Take. | No | integer |
| take | query | OPTIONAL. Takes only the first .. rows of meta information. The opposite of Skip. When not specified the API tries to get all rows. | No | integer |
GET /v1/CalibrationData
Responds with the complete calibration data in JSON form. See filter parameters. The query can be filtered. See filter parameters.
GET /v1/CalibrationData/Export
Exports the filtered calibration data as ZIP (or BROTLI) file with the calibration files (JSON). As a result, a download link is replied. Brotli-file-type is not supported as of now.
| Name | Located in | Description | Required | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fileType | query | 1 = All calibration data items will be merged in one JSON list 2 = All calibration data items will be merged in one JSON list. This JSON file will be compressed to zip file 3 = Every calibration data items will stored as JSON file. All these files will be compressed to one single zip file 4 = Every calibration data items will stored as JSON file. All these files will be compressed to one single brotli file | No | ExportFileType |
plus all filter parameters
GET /v1/CalibrationData/Count
Get the count of the calibration data set based on the optional search parameters. See filter/search parameters. If optionalSearchParameter or its fields are null then the returned number is the amount of all sensors the account has access to. You can use this to quickly find out how many files you request with a given query.
GET /v1/CalibrationData/List
Get a list of all identifier strings of the calibration data set defined by the optional search parameters. See filter/search parameters. These identifier strings (IncludedIds) can then used as input as filter parameter for a query in GET /v1/CalibrationData
GET /v1/CalibrationData/New
Get a list of all data that is stored in myCalibration after given datetime since. Data is stored in myCalibration mostly, 1 day before the start of the delivery from Switzerland. This correlates with the dispatch date but differs often.
| Name | Located in | Description | Required | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| since | query | UTC DateTime - Responses contain all data younger than this moment | Yes | integer |
PUT /v1/CalibrationData/New
WARNING: Only use when you know what you do. Better ask engineering@keller-pressure.com Gathers all NEW data. ‘New data’ is calibration data that was never requested with this request. A second request might return an empty list. Optionally, if the new data could not be stored, then with ‘countOfHoursDataWasAlreadyRequested’ the data requested will be shown again back to the given hours. Optionally, ‘countOfHoursDataWasAlreadyAssigned’ can be used
| Name | Located in | Description | Required | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| take | query | No | integer | |
| countOfHoursDataWasAlreadyRequested | query | No | integer | |
| countOfHoursDataWasAlreadyAssigned | query | No | integer |
MefistoViewModel
Mefisto = MEtainfo for FIle STOrage Example:
{
"id": 28651,
"customerName": "DemoData Inc.",
"customerNumber": 12345678,
"subCustomerNumber": 0,
"remarks": "",
"serialNumber": "23650",
"productNumber": "123856.1113",
"productType": "PA-23R",
"pressureType": "Pa",
"productSeries": "23R",
"compensatedTemperatureRangeMin": 15.0,
"compensatedTemperatureRangeMax": 70.0,
"compensatedTemperatureRangeUnit": "C",
"compensatedPressureRangeMin": 0.0,
"compensatedPressureRangeMax": 1.0,
"compensatedPressureRangeUnit": "Bar",
"electricSupplyMin": 4.5,
"electricSupplyMax": 24.0,
"electricSupplyMagnitude": 0.0,
"electricSupplyUnit": "V",
"orderNumber": 9990740,
"orderPosition": 1,
"orderTargetDispatchDate": "2017-05-26T00:00:00",
"customerOrderNumber": "Cust-9990740-123",
"customerReferenceNumber": "ABC",
"customerProductType": "123451-1113",
"subCustomerOrderNumber": null,
"subCustomerOrderPosition": null,
"assignedToSubCustomerDateUtc": null
}
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Integer | internal id |
| CustomerName | String | Customer name |
| CustomerNumber | Integer | KELLER customer identification number |
| SubCustomerNumber | Integer | KELLER customer identification number for a customer of a customer |
| Remarks | String | File creation date (UTC) |
| SerialNumber | String | KELLER product serial number |
| ProductNumber | String | KELLER product number |
| ProductType | String | KELLER product type |
| PressureType | String | KELLER product pressure type |
| ProductSeries | String | KELLER product series |
| CompensatedTemperatureRangeMin | Double | Temperature range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated Min |
| CompensatedTemperatureRangeMax | Double | Temperature range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated Max |
| CompensatedTemperatureRangeUnit | String | Temperature range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated U nit |
| CompensatedPressureRangeMin | Double | Pressure range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated Min |
| CompensatedPressureRangeMax | Double | Pressure range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated Max |
| CompensatedPressureRangeUnit | String | Pressure range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated Unit |
| ElectricSupplyMin | Double | Nominal electric supply Min |
| ElectricSupplyMax | Double | Nominal electric supply Max |
| ElectricSupplyMagnitude | Double | Nominal electric supply Magnitude |
| ElectricSupplyUnit | String | Nominal electric supply Unit |
| OrderNumber | Integer | KELLER purchase order number |
| OrderPosition | Integer | KELLER purchase order position |
| OrderTargetDispatchDate | Date | Targeted dispatch date of the order |
| CustomerOrderNumber | String | Customer internal purchase order number |
| CustomerReferenceNumber | String | Customer internal reference number |
| CustomerProductType | String | Customer internal product type |
| SubCustomerOrderNumber | String | Invoice Number from the Customer for the SubCustomer |
| SubCustomerOrderPosition | String | Additional order details for the SubCustomer from the Customer. Eg."Invoice Line" |
| AssignedToSubCustomerDateUtc | Date | Timestamp of the moment the data was assigned to a sub customer |
Filter parameters
| Name | Located in | Description | Required | Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IncludedIds | query | If null: Either are ‘ALL SELECTED’ or some are unselected (and listed in ExcludedIds) If not null: None are selected except those that are listed here. It is not allowed to have IncludedIds AND ExcludedIds have listed values. One most be null or both most be null. The list of included ids is limited to 50. More than 50 will throw an exception. |
No | [ string ] |
| ExcludedIds | query | If null: Either are ‘ALL SELECTED’ or only some few are selected (and listed in IncludedIds) If not null: All are selected and except those that are listed here. It is not allowed to have IncludedIds AND ExcludedIds have listed values. One most be null or both most be null. The list of excluded ids is limited to 50. More than 50 will throw an exception. |
No | [ string ] |
| OrderNumbers | query | List of Order Numbers | No | [ string ] |
| OrderPositions | query | List of Order Positions | No | [ string ] |
| DateFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘DateTo’ is needed. Example 1: “All data newer than August 1st” = https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData?DateFilterType=greaterThan&Date=2021-08-01 Example 2: “All data from the year 2020” = https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData?DateFilterType=inRange&Date=2021-01-01&DateTo=2021-12-31 Example 3: “All data from the first day in January and February” = https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData?DateFilterType=equals&Date=2021-01-01&Date=2021-02-01 |
No | string |
| Date | query | Dispatch-date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” Normally, this is a list with one element. Nevertheless, it is possible to GET calibration data from multiple dates. In this case DateFilterType must be ‘equals’ and DateTo must be null. |
No | [ string ] |
| DateTo | query | Used when DateFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘Date’ to ‘DateTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” |
No | string |
| CustomerProductTypes | query | To search for [Blanks] use “blank” | No | [ string ] |
| PressureTypes | query | Eg. [“pa”,”paa”,”pr”] To see all possible enum strings, go to https://mycalibration.github.io/#filter-parameters | No | [ string ] |
| ProductSeries | query | Eg. [“10LHP”,”25Y”,”46X”,”K-102”] | No | [ string ] |
| ProductNumbers | query | No | [ string ] | |
| SerialNumberSearchText | query | Use this to find all SerialNumbers that contains this text content. | No | string |
| PressureMinFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘PressureMinTo’ is needed. |
No | string |
| PressureMin | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Minimum Pressure” | No | double |
| PressureMinTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Minimum Pressure”. Used when PressureMinFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘PressureMin’ to ‘PressureMinTo’. Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” |
No | double |
| PressureMaxFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘PressureMaxTo’ is needed. |
No | string |
| PressureMax | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Maximum Pressure” | No | double |
| PressureMaxTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Maximum Pressure” Used when PressureMaxFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘PressureMax’ to ‘PressureMaxTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” |
No | double |
| PressureUnit | query |
|
No | [ string ] |
| TemperatureMinFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘TemperatureMinTo’ is needed. |
No | string |
| TemperatureMin | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Minimum Temperature” | No | double |
| TemperatureMinTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Minimum Temperature” Used when TemperatureMinFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘TemperatureMin’ to ‘TemperatureMinTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” |
No | double |
| TemperatureMaxFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘TemperatureMaxTo’ is needed. |
No | string |
| TemperatureMax | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Maximum Temperature” | No | double |
| TemperatureMaxTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Maximum Temperature” Used when TemperatureMaxFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘TemperatureMax’ to ‘TemperatureMaxTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” |
No | double |
| TemperatureUnit | query |
|
No | [ string ] |
| SupplyMinFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘SupplyMinTo’ is needed. Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | string |
| SupplyMin | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Minimum Supply” Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyMinTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Minimum Supply” Used when SupplyMinFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘SupplyMin’ to ‘SupplyMinTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyMaxFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘SupplyMaxTo’ is needed. Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | string |
| SupplyMax | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Maximum Supply” Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyMaxTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Maximum Supply” Used when SupplyMaxFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘SupplyMax’ to ‘SupplyMaxTo’ Date text in format ‘yyyy-MM-dd’ eg. “2021-12-24” Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyMagnitudeFilterType | query | One of ‘equals’, ‘greaterThan’, ‘lessThan’, ‘notEqual’, ‘inRange’, ‘lessThanOrEqual’, ‘greaterThanOrEqual’. When ‘inRange’ then ‘SupplyMagnitudeTo’ is needed. Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | string |
| SupplyMagnitude | query | The exclusive lower bound of the “Supply Magnitude” Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyMagnitudeTo | query | The exclusive upper bound of the “Supply Magnitude” Used when SupplyMagnitudeFilterType is ‘inRange’. Data is gathered from ‘SupplyMagnitude’ to ‘SupplyMagnitudeTo’ Either Min/Max is used or Magnitude. |
No | double |
| SupplyUnit | query |
|
No | [ string ] |
| CustomerReferenceNumberSearchText | query | Find all data with contains this search text | No | string |
| CustomerOrderNumberSearchText | query | Find all data with contains this search text | No | string |
| RemarksSearchText | query | Find all data with contains this search text | No | string |
Filter parameters - PhysicalUnits & PressureTypes
Filter parameters - PhysicalUnits : PressureUnit, TemperatureUnit, SupplyUnit
Although ‘%FS’ is shown in the UI and listed in the JSON, the API parameter string used is ‘Fs’.
________________________
| | |
| Unit | API string |
|__________|_____________|
| %FS | Fs |
| A | A |
| K | K |
| MOhm | MOhm |
| MPa | MPa |
| Ohm | Ohm |
| Pa | Pa |
| Torr | Torr |
| V | V |
| VDC | VDC |
| atm | Atm |
| bar | Bar |
| cmH2O | CmH2O |
| cmHg | CmHg |
| ftH2O | FtH2O |
| hPa | HPa |
| inH2O | InH2O |
| inHg | InHg |
| kN/m2 | KNM2 |
| kOhm | KOhm |
| kPa | KPa |
| kp/cm2 | KpCm2 |
| lbf/ft2 | LbfFt2 |
| mA | MA |
| mH2O | MH2O |
| mV | MV |
| mV/V | MVV |
| mV/mA | MVMA |
| mbar | Mbar |
| mmH2O | MmH2O |
| mmHg | MmHg |
| psi | Psi |
| °C | C |
|________________________|
Filter parameters - PressureTypes
Although ‘PA’ is shown in the UI and listed in the JSON, the API parameter string used is ‘Pa’.
______________________
| | |
| Unit | API string |
|________|_____________|
| PA | Pa |
| PAA | Paa |
| PD | Pd |
| PR | Pr |
| PRD | Prd |
|______________________|
Example queries
Please see https://github.com/mycalibration/mycalibration.github.io
Generate client SW using the OpenAPI/swagger schema
Use https://editor.swagger.io/ The Swagger/Openapi import URL is here: https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/swagger/v1/swagger.json
Accessing the API with the Permanent Access Token
There are two types of tokens. The Permanent Access Token and the Temporary Access Token.
With the Temporary Access Token it is possible to access the data via API using the Swagger/OpenAPI UI. This is working for a couple of hours after login.
The Permanent Access Token is used to access the API programmatically without manual login.
Temporary Access Token
Get the Temporary Access Token form the Profile Settings:
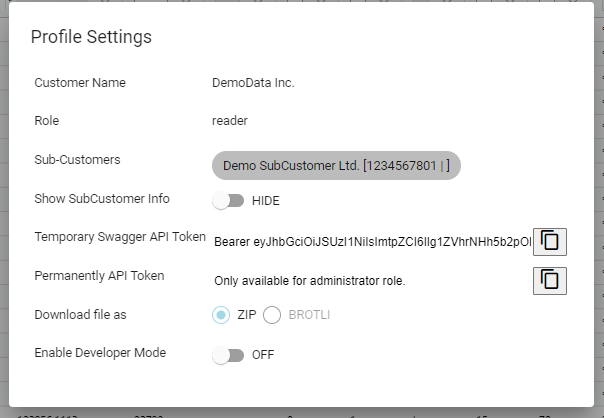
In the Swagger/OpenAPI UI click on the Authorize button and enter the Temporary Access Token:
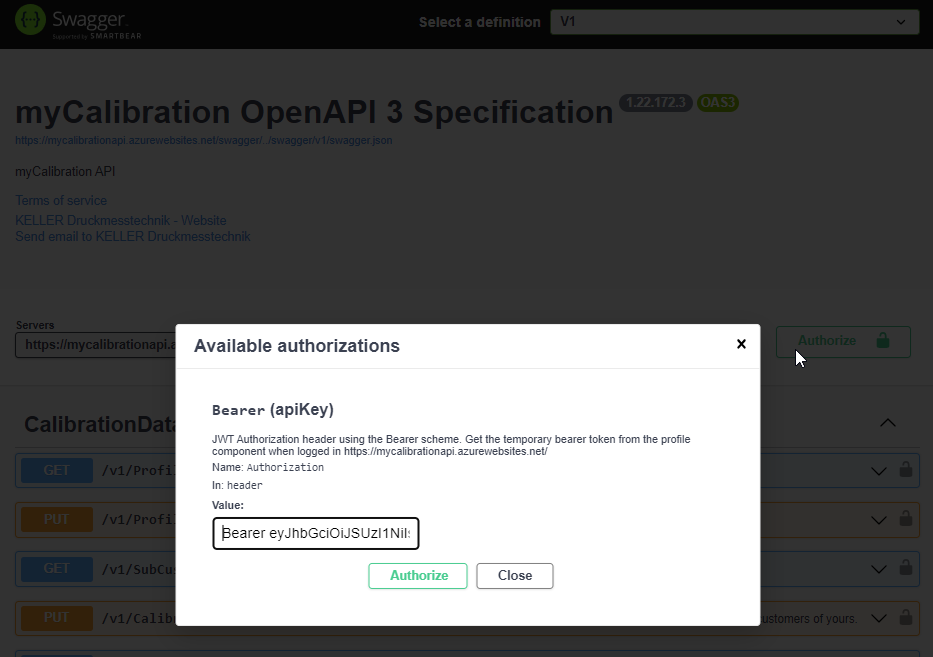
Permanent Access Token
As of now, you have to request the the Permanent Access Token directly from KELLER’s myCalibration Support Team : engineering@keller-pressure.com
The provided access token must be the value with the key ‘userOid’ in the header of every request. This way a bearer token and the OAuth 2 flow is NOT needed anymore.
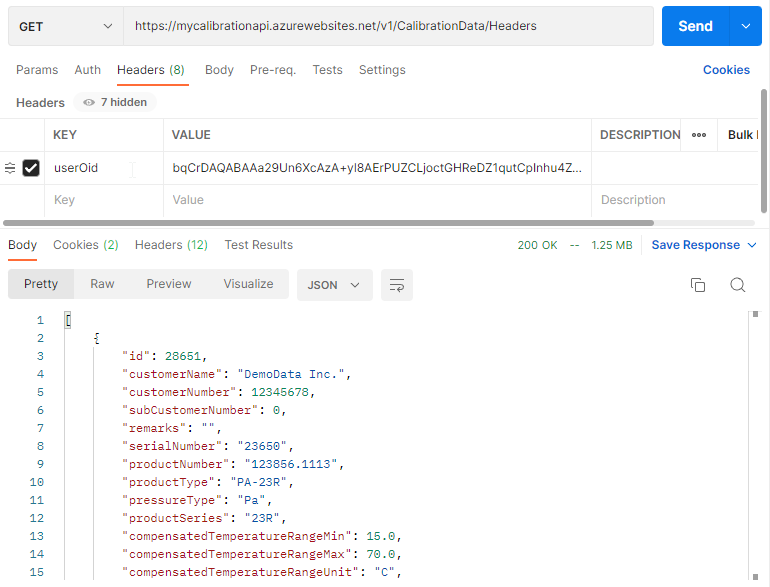
Use tools like Postman, Insomnia or curl to test the API.
There are many programming examples on Github.
Here an example in C#:
var url = "https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Headers";
var httpRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
// Add the permanent access token to the header with the userOid key
httpRequest.Headers["userOid"] = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR....";
string resultJsonText;
HttpWebResponse httpResponse = (HttpWebResponse)httpRequest.GetResponse();
using (var streamReader = new StreamReader(httpResponse.GetResponseStream()))
{
resultJsonText = streamReader.ReadToEnd();
}
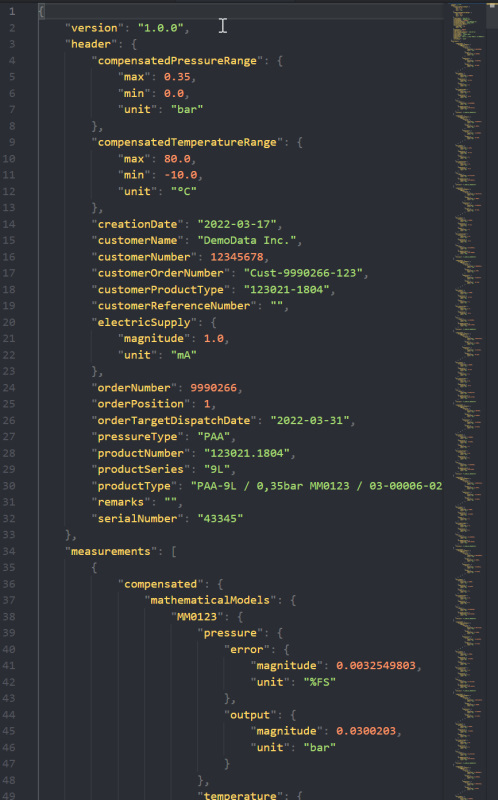
4) The JSON Schema
The schema can be downloaded as JSON Schema here. And converted to various other file types here.
| Root objects | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Version | Version string for the schema with semantic versioning (MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH) E.g. “1.0.0” |
| Header | Meta-information data to identify the sensor data |
| CompensationMethods | MathMod data |
| Measurements | Measurements point of the T/P-calibration-curve |
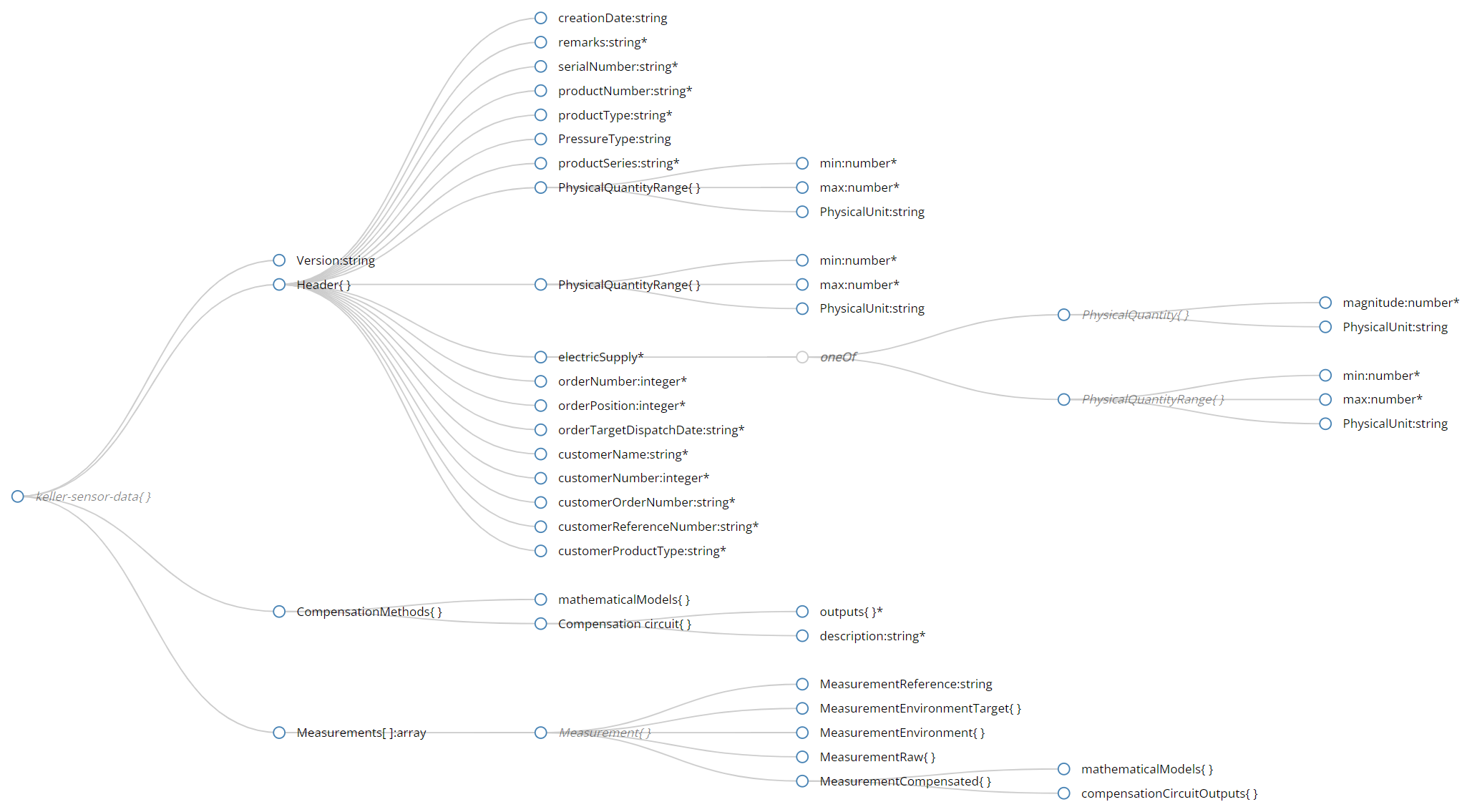
| Root object | Object | Schema Description | Explanation | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| version * | Version of the corresponding JSON Schema | Version for the schema with semantic versioning (MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH) | string | "1.0.0" | |
| header * | Header data | Meta-information to identify and catalogize the calibration data stored in measurements | |||
| creationDate | File creation date | string | "2022-03-22" | ||
| orderTargetDispatchDate * | Targeted dispatch date of the order | string | "2022-03-15" | ||
| orderNumber * | KELLER purchase order number | int | 9990016 | ||
| orderPosition * | KELLER purchase order position | int | 3 | ||
| customerProductType * | Customer internal product type | string | "9990016-123" | ||
| pressureType * | Pressure type | string | "PAA" | ||
| productSeries * | KELLER product series | string | "33X" | ||
| productType * | KELLER product type | string | "PAA-33X" | ||
| productNumber * | KELLER product number | string | "1234567.0001" | ||
| serialNumber * | KELLER product serial number | string | "I123456" | ||
| compensatedPressureRange * | Pressure range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated | object | {"max": 1.0,"min": 0.0,"unit": "bar"} | ||
| compensatedTemperatureRange * | Temperature range over which the sensors characteristics have been compensated | object | {"max": 70.0, "min": 15.0, "unit": "°C"} | ||
| electricSupply * | Nominal electric supply | |
object | {"unit": "V","max": 24.0,"min": 4.5} or {"unit": "mA","magnitude": 1.0} | |
| customerReferenceNumber * | Customer internal reference number | string | "Jane Doe" | ||
| remarks * | string | "" | |||
| customerName * | Customer name | string | "DemoData Inc." | ||
| customerNumber * | KELLER customer identification number | string | "9990016 Rev. 2" | ||
| customerOrderNumber * | Customer internal purchase order number | "123456700012" | |||
| measurements[]* | Array of individual measurements. Item order corresponds to order in measurement sequence. | Array of Measurement | |||
| reference * | KELLER reference to original measurement data | string | "TSX_ABCD567P89" | ||
| environment * | Real conditions of the measurement point environment | object | { "pressure": { "magnitude": 0.1000031, "unit": "bar" }, "temperature": { "magnitude": 14.6304, "unit": "°C" }, "barometer": { "magnitude": 0.970963, "unit": "bar" } } |
||
| environmentTarget | Target conditions of the measurement point environment | object | { "pressure": { "magnitude": 0.1, "unit": "bar" }, "temperature": { "magnitude": 15, "unit": "°C" } } |
||
| raw | Raw measurement values | object | { "bridgeResistance": { "magnitude": 3391.10116554, "unit": "Ohm" }, "signal": { "magnitude": 24.238461872, "unit": "mV" } } |
||
| compensated | Compensated measurement data by different compensation methods | |
object | { "compensationCircuitOutputs": { "P1": { "measuredValue": { "magnitude": 0.03000106, "unit": "bar" }, "nominalValue": "magnitude": 0.02999711, "unit": "bar" } }, "TOB1": { "measuredValue": { "magnitude": 14.59302, "unit": "°C" }, "nominalValue": { "magnitude": 14.6313, "unit": "°C" } } } |
|
| compensationMethods | Information on different compensation methods | ||||
| mathematicalModel | A mathematical compensation model | object | { "MM0324": { "compensatedPressureRange": { "max": 0.35, "min": 0.03, "unit": "bar" }, "compensatedTemperatureRange": { "max": 80.0, "min": -10.0, "unit": "°C" }, "electricSupply": { "magnitude": 1.0, "unit": "mA" }, "modelType": "MM0324", "parts": { "pressure": { "coefficients": [[1.8578428692012365, -0.0017637338444390805, 6.089070597524738E-07, -9.469256273591509E-11, 5.4899128873639585E-15], [-0.0972735455799812, 0.00010464739112826799, -3.9404534306891384E-08, 6.5906859977677644E-12, -4.1433054700020206E-16], ... etc. ] "description": "P = f(Sig,R)", "inputs": ["Sig", "Rb"], "output": "P" }, "temperature": { "coefficients": [[-7875.716974895135, 4.720765539450497, -0.036522641391128374], [7.760050026358172, ...etc. ],], "description": "T = f(R,Sig)", "inputs": ["Rb", "Sig"], "output": "T" } } } } |
||
| compensationCircuit | Compensation circuit | object | { "outputs": { "P1": { "description": "Pressure 1" }, "TOB1": { "description": "Temperature 1" } }, "description": "5432109.0004" } |
5) Sample Software
Github repo: https://github.com/mycalibration/mycalibration.github.io/
- /docs - Content of the documentation page https://mycalibration.github.io/
- /samples
- /api
- /csharp-dotnet/simple - Simple C# example to show how to get data from the API and parse it.
- /csharp-dotnet/swagger-codegen - Auto-Generated code based of the OpenAPI file. Generated on /editor.swagger.io
- /python/simple - Simple Python example to show how to get data from the API and parse it.
- /python/swagger-codegen - Auto-Generated code based of the OpenAPI file. Generated on editor.swagger.io
- /labview/simple - LabView example to show the API access via permanent access token and how to extract data out of the response.
- /data-model/KellerSensorData.cs - C# class with the data schema structure implemented.
- /json-to-csv
- /json-to-csv-converter - Converter source to demonstrate the conversion from the JSON data to the old obsolete text/CSV file data.
- /ConverterUsageSample/Program.cs - Example usage of the converter.
- /OnlineConverterBlazorApp - Another example usage of the converter by creating a Blazor Web Assembly App that converts the JSON to the old text files.
- /combined/WinFormsApp - Windows Forms Demo app (C# with .NET6) to show how to get data from the API, convert the result to an C# object and convert the calibration data to the old obsolete text/CSV file data using the /json-to-csv-converter
- /api
-
/schema/keller-sensor-data.schema.json - The myCalibration JSON schema
- Online ‘JSON to old text files’-converter : https://mycalibration.github.io/converter
6) FAQ
-
Can I try out the «myCalibration» service?
Yes. Use the user ‘Demo1234’ and its password ‘Demo1234’. This gives you access to a demo account with some valid demo data. -
How can I automatically download the data and store it into my database / SCADA / file system?
Use the Web API (https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/) and a permanent access token to access the data on-demand via REST API queries. The SW for this is not complicated. Use meaningful filter parameter and load the data periodically. -
What is the easiest way to develop software to download the data?
There is open-sourced sample SW on https://github.com/mycalibration/mycalibration.github.io/
Use the swagger UI and a temporary access token to get yourself familiar with the filter parameters.
Use the swagger file to generate a client SW in your preferred language using generator-SW such as https://editor.swagger.io/ (C#, Go, HTML, Java, Javascript, Python, PHP, Scala, Typescript…) -
I have the JSON file. How do I parse these files to extract the information I need?
The JSON files underlie a JSON schema. This schema can be used to generate code artifacts that help to parse the information. See https://json-schema.org/implementations.html#generators-from-schemas
We used https://app.quicktype.io/ to generate the C# data classes that makes it easy to deserialize the JSON. As an example, the JSON data is parsed and converted to the old txt/CSV files in the converter example. - How do I find new data? Is there a notification system?
No, there is no notification system. You have to periodically ask the API for new data.
Unfortunately, it is also not that easy to find new data. There are some ways:- Periodically, check the number of calibration data. If the number is higher then try to find new data. (Use
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Count) - Just load all metadata (
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/Headers) and compare it with the data you already downloaded and stored (using the ProductNumber and the SerialNumber). - Be aware that the Dispatch-Date is not a good way to filter for new data. It is the supposed date for the delivery. In reality, it might be that an order was produced and sent earlier than another order with a even earlier dispatch date.
- Another way is to use the
PUT <https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/New. When using this endpoint, it response with all new data. Be aware that when requesting this data then the data is marked and manipulates internally. Hence thePUT. A second request shortly after the first will response without data. - Another way is to store the ids (identifier strings), get the list of all identifier strings and compare & search for new ones. If there are new ones than just download them with
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData?IncludedIds=12345&IncludedIds=12346as an example. - There is also
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Newand with the required DateTime parameter. You will get back the list of data that was newly ingested from the given moment (UTC). - To combine the two ideas above, there is also
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/List/Newthat responds with a list of identifier strings that are newer than a certain given DateTime (UTC). Use this list to synchronize with your stored data using the identifier strings as a lookup key. An example call looks like this:GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/List/New?since=2023-04-01T12:15:00.000Z
- Periodically, check the number of calibration data. If the number is higher then try to find new data. (Use
- What are best practices when using the API? What endpoints should I use?
Generally, there should be two steps:- Periodically load new data and store it into your DB/file system.
- Extract the coefficients (and more information) from the JSON and store it or use it to program your firmware with the sensor.
- Use the count request to check if you have the same amount of data stored
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/CountOtherwise, download the data. - Alternatively, you can download all the meta information from
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Header. These are the fields you see in the web app columns. - When downloading data, you can filter for all the meta information. This is how the web app works. Enable the ‘Developer Mode’ to see the used filter parameter and the resulting API call.
- Downloading data is best made with the
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationDatacall. It responses with a list of all filtered JSON files. - If you have a list of serial numbers you can use the serial number as a filter parameter and download each JSON content individually
- It is not recommended to use the
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Exportquery. Prefer to download the content directly withGET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData - The myCalibration API might not work 100%. Consider appropriate reactions in case an API query is not responding and try the query later.
- Use the count request to check if you have the same amount of data stored
-
What makes files unique? Is the serial number enough for an identification?
Generally, product-number and serial-number should good enough to define a unique sensor data set. Nevertheless, a JSON file looks like this:{Product Number}_{Serial Number}_{File Creation Date}_{MathMod Number}.jsonEg. 100715.0244_X12345_2023-04-06_0123.json
In rare cases, a sensor is send back to us for re-calibration. This is why the file creation date is included in the file name. Some customer buy sensors from KELLER with multiple MathMod (most probably because they have different use cases with different pressure/temperature ranges) and for this, the MathMod number is included, too. In this case, two files are created for each MathMod. -
What happens when I have multiple entries with the same serial number? This might happen when a sensor is send back to us for reparation or re-calibration. In this case, the serial number is not unique anymore. Multiple entries with the same serial number can be found in the Web App or API call. The correct entry is the most recent and can be identified by the ‘File Creation Date’ column.
-
How can I get only ‘new’ data from the API? Instead of
GET https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationDatato get ALL data, usePUT https://mycalibrationapi.azurewebsites.net/v1/CalibrationData/Newto get only the newest data not requested before. This request will mark the data as ‘requested’ and will not be returned again with the nextPUTrequest. Except when using the optional parameterscountOfHoursDataWasAlreadyRequestedorcountOfHoursDataWasAlreadyAssignedwhich can again override the ‘requested’ state for a given time span. -
Where can I see the Terms & Conditions?
myCalibration Terms and Conditions -
I tried the converter. It does not give me the 1:1 data as the TXT file I am used to. Why?
The converter was build as a proof-of-concept in order to show that nearly all information in the TXT/CSV files are also stored in the JSON file. It is not meant as a 1:1 conversion and should not be used in production. -
But I use these TestRun.txt and ….CSV files for years. Why should I change to the JSON file?
Changing to the JSON files is not that difficult for a developer given the many examples. The converter example shows how to access the JSON data and extract the needed (coefficients) data. The online converter also demonstrates the possibility to extract the needed data from the JSON files. -
Is this platform secure? Are any standards used?
Yes. Customer data is only accessible after an individual login and cannot be seen by others. Thanks to best practices, audits and Microsoft’s ‘Azure Active Directory B2C’ authentication technology, security is guaranteed.The «myCalibration» platform uses the access, storage and authentication of users and data in/from a MICROSOFT (Azure) data center. This data center is in the EU and subject to EU regulations ( EU Data Protection Regulation [DSGVO] ). https://www.microsoft.com/de-de/TrustCenter/Privacy/gdpr/default.aspx Be aware that there is no relevant ‘personal data’ stored. What standards does Microsoft guarantee?
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/overview/trusted-cloud/ (overview) https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/microsoft-azure-leads-the-industry-in-iso-certifications/ (overview) List of standards: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/trustcenter/compliance/complianceofferings eg ISO 9001 , ISO 20000-1: 2011, ISO 2230, ISO 27001, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, BIR 2012 (Netherlands), UK G-Cloud, Argentina PDPA …
-
Where do I get a permanent access token from to access the API?
The temporary and permanent access token can be seen in the web app under “Profile Settings” which can be found with the button of the company name.
There is always the temporary access token that can be used for the Swagger/OpenAPI UI.
If the permanent access token is not visible for you then you might need to be given the needed authorization from engineering@keller-pressure.com. Ask for an permanent access token. -
How do I USE the permanent access token access the API?
See Accessing the API with the Permanent Access Token
7) Roadmap
- Update Documentation / Schema
- Update release notes and planned maintenance windows
- Description of new “Pressure Line Dependency”remark
8) Release Notes
See Release Notes